Global Temperature Changes
Earth's temperature has risen significantly since the pre-industrial era, with the last decade being the warmest on record.
Key Statistics
Temperature Increase Since 1880
0.0°C
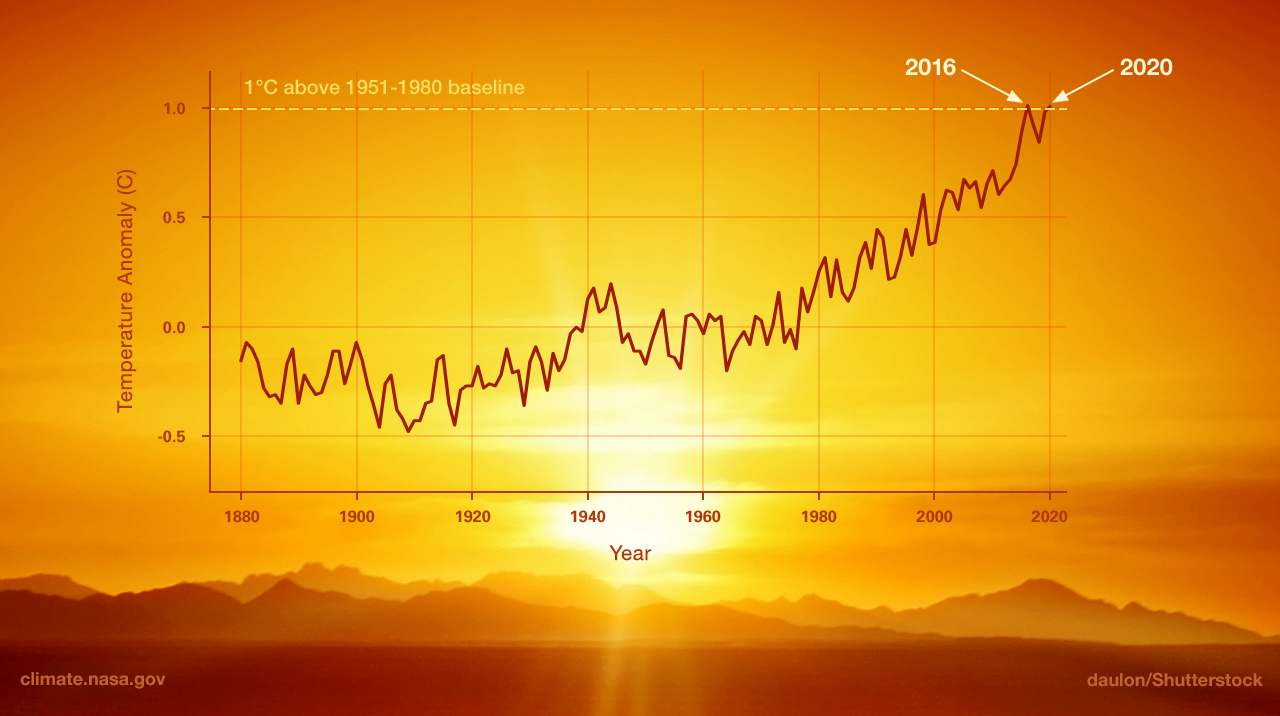
Global temperature has increased by at least 1.1°C since 1880, with most warming occurring since 1975.
2024 Temperature Anomaly
0.00°C
2024 was the warmest year on record, with Earth's average surface temperature approximately 1.28°C above the 1951-1980 baseline.
Warming Rate Per Decade
0.00°C
The current rate of warming is approximately 0.15-0.20°C per decade, significantly faster than historical rates.
Global Temperature Trends
Data source: NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS). Temperature anomalies relative to the 1951-1980 average.
Global Temperature Change Visualization
NASA's visualization of global temperature change from 1880 to present. The blue colors represent temperatures below the 1951-1980 average, while red colors represent temperatures above the average.
Causes and Impacts
Primary Causes
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes that release CO₂, methane, and other heat-trapping gases.
- Land Use Changes: Deforestation and urbanization reduce the Earth's ability to absorb carbon dioxide.
- Industrial Processes: Manufacturing, agriculture, and other human activities that release greenhouse gases.
Key Impacts
- Extreme Weather: More frequent and intense heatwaves, droughts, floods, and storms.
- Sea Level Rise: Melting ice sheets and glaciers, plus thermal expansion of seawater, causing coastal flooding.
- Ecosystem Disruption: Shifts in species ranges, changes in migration patterns, and increased extinction risk.
- Human Health: Heat-related illnesses, expanded range of disease vectors, and food/water insecurity.
Future Projections
Even under the lowest possible greenhouse gas emissions pathway (limiting warming to 1.5°C), significant additional warming is inevitable. Under high emission scenarios, global temperatures could rise by 4°C or more by 2100, with catastrophic consequences for ecosystems and human societies.
Low Emissions Scenario
1.5-2.0°C warming by 2100
Requires immediate, dramatic emissions reductions
Medium Emissions Scenario
2.0-3.0°C warming by 2100
Based on current policies and pledges
High Emissions Scenario
3.0-5.0°C warming by 2100
Business-as-usual with minimal climate action